Anxiety & Depression
Anxiety is a sense of unease or fear that is unpleasant and can range from moderate to extreme. Everyone feels nervous and it is natural at some stage in their life, but anxiety can become more difficult to manage for some people and it can get in the way of their everyday lives. In certain situations, rather than becoming more generic anxiety, this out of control anxiety may be based on a particular situation, and this is often considered situational anxiety.
Depression is not the same for all, there are several forms, and individuals undergo this treatable disorder with different degrees of seriousness.
Nonpharmacological treatments such as psychotherapy, dietary improvements, and herbal treatments can be responsible for raising the gloom and relieve symptoms for certain individuals with depression.
What does ANTI-ANXIETY PILLS (Benzodiazepines) do?
Anti-Anxiety pills enhance the activity of the brain that helps you to feel calm.
Their effect also produces drowsiness, making it easier to fall asleep and sleep through the night.
Benzodiazepines
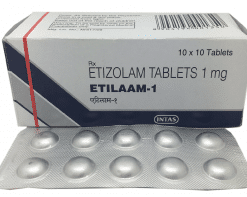
Anti-anxiety medications specifically target the fear and worry of anxiety, and a class of medications called benzodiazepines are the most common form of anti-anxiety drugs.2 Benzodiazepines have many advantages, including their quick onset of action and efficacy, but they carry substantial risks as well.
Compared to antidepressants, benzodiazepines take effect very quickly. In some cases, people may feel the calming and relaxing benefits of these drugs just minutes after use.5
Rather than acting on serotonin or norepinephrine, benzodiazepines interact with another neurotransmitter called GABA, short for gamma-aminobutyric acid. GABA inhibits signaling in the brain and influences sleep, muscle relaxation, feeling calm, and slows brain activity.5
Examples of benzodiazepines include:4
- alprazolam (Xanax)
- clonazepam (Klonopin)
- diazepam (Valium)
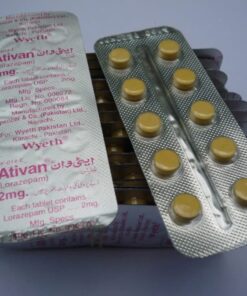
- lorazepam (Ativan)
Detractors of benzodiazepines point to unwanted issues that may present if these drugs are used for longer periods of time than intended. In a process called tolerance, someone using benzodiazepines may need higher doses of the drug to maintain the same benefit over time. Over time, the brain may become physically dependent on these medicines to feel well and function normally. Physical dependence may lead to addiction, where a person becomes obsessively focused on getting and using the medication
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY
ANTI ANXIETY